Periodontal Treatment
If you feel your gums are bleeding or sore you may be suffering from gum disease(gingivitis or periodontitis).
While there are many forms of gingival and periodontal diseases, the most common types are gingivitis and adult periodontitis.
Gingivitis is the earliest stage and affects only the gum tissue. At this stage, the disease is still reversible. If not treated, however, it may lead to a more severe condition.
Periodontitis is the more advanced stage of periodontal disease. The gums, bone and other structures that support the teeth become damaged. Teeth can become loose and fall out-or may have to be removed. At this stage, the disease may require more complex treatment to prevent tooth loss.
The treatment for early stages of periodontitis is relatively simple and cost effective. Treating the gum infection early will prevent further bone loss and tooth extractions. Bacteria from infected gums can travel through your blood system and cause chronic infections in different organs, this is specially a concern in pregnant women.
Here is a step-by-step illustration of the process of gingivitis to periodontitis:

Although gum diseases are caused by plaque, a number of other factors can increase the risk, severity, and speed of development of the condition.
- People who smoke or chew tobacco are more likely to have gum diseases, and to have them more severely, than those who do not use any form of tobacco.
- Poorly fitting bridges, malocclusion (badly aligned teeth) or defective restorations (fillings), can all contribute to plaque retention and increase the risk of developing gum disease.
- Habits which place excessive biting forces on your teeth, such as clenching or grinding, may also accelerate the rate at which supporting bone is lost.
- Poor diet may cause gum diseases to progress more rapidly or increase the severity of the condition, according to some researchers. There is also some evidence than an unbalanced diet makes mouth tissues less resistant to infection.
- Pregnancy or the use of oral contraceptives increases hormone levels which can cause gum tissues to react more intensely to the toxins in plaque and accelerate growth or certain bacteria. The gums are more likely to become red, tender, and swollen and to bleed easily.
- Systemic diseases, such as AIDS or diabetes, can lower the tissues’ resistance to infection, making gum diseases more severe.
Symptoms
In most cases periodontal disease goes unnoticed on its early stages. Once discomfort arises the disease has advanced considerably and permanent bone loss has occurred. If you wait until it hurts it may be too late for some of your teeth.
- Early Stages: Redness, tenderness, swelling, and bleeding gums
- Late Stages: Shrinking of gums, loose teeth, bad mouth odors and pus drainage.
How Gum Disease is Treated
The treatment will depend in what stage you are in. Dentist will recommend procedures that will range from: a regular cleaning, deep cleanings with anesthesia, adjustment of bite, antibiotics, prescription mouth rinses or minor surgery.
In most cases of periodontitis the starting treatment will consist in scaling and root planning (deep cleanings). For this procedure Dr. Garcia will make sure the area is anesthetized, that way she’ll be able to clean the infected tartar thoroughly with no discomfort to you. This is a diagram of how it works:
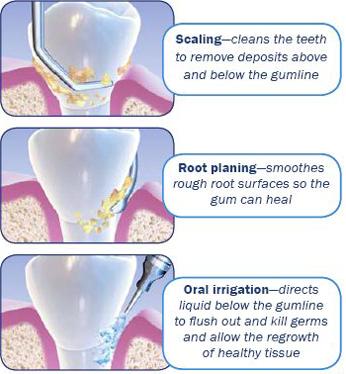
After the Scaling and Root Planning the patient will require periodic cleaning, called Periodontal Maintenance, every three months. By doing this we make sure the disease does not recur, keeping your oral tissues healthy for years to come.
Periodontal Surgery
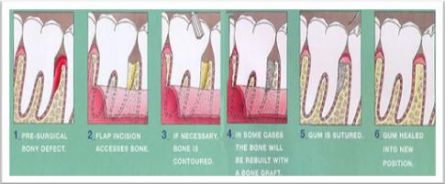
In a small percent of the cases additional treatment is required to completely remove the infected tartar and tissues. It will consist of a minor surgery to gain access to the affected site.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Periodontal treatment is a two-way process. The dentist will do her share by professionally removing all the tartar and infected tissues, but the patient needs to be compliant at home and at regular cleanings to prevent the disease from recurring. This is what you can do:
- Regular, professional cleanings of the mouth at the dentist’s office.
- Meticulous attention to home care, flossing and brushing.
- Don’t wait until it hurts.
- Have at least yearly check-ups to diagnose systemic diseases, as diabetes, on its early stages.
- Do not smoke
